3. 抛物方程#
3.1. 固定区域#
Consider the equation with Dirichlet boundary conditions
(3.1)#\[\begin{equation}
\left\{
\begin{aligned}
&u_t - a\Delta u + (b \cdot \nabla) u- f = 0 \\
&u_0 = \phi(x) \\
&u_{\Gamma} = g(x)
\end{aligned}
\right.
\end{equation}\]
on \(\Omega = [0, 1]^2\) with
(3.2)#\[\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
&f = 0, \\
&g = 0, \\
&a = 1/(2\pi^2),\\
&b = (0, 0),\\
&\phi(x) = \sin(\pi x)\sin(\pi y). \\
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}\]
The variational form is
(3.3)#\[\begin{equation}
F := (\frac{u^{n+1} - u^n}{\tau}, v) + (a\nabla u^{n+1}, \nabla v) + (b\cdot\nabla u^{n+1}, v) - (f^{n+1}, v) = 0
\end{equation}\]
3.1.1. Step to solve the problem#
Define the domain/mesh
Create function space on the domain
Define the variational problem
Define the variational form
Define the boundary conditions
Define the variational solver
Solve the problem in a time loop
from firedrake import *
from firedrake.pyplot import tricontourf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_solution(u_h, time=None, vmin=None, vmax=None):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=[5, 4])
if vmin is None or vmax is None:
levels = None
else:
levels = np.linspace(vmin, vmax, 11)
cs = tricontourf(u_h, axes=ax, levels=levels)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlabel('$x$')
ax.set_ylabel('$y$')
if time is not None:
ax.set_title(f'$t={time}$')
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs)
N = 32
M = 32
T = 1
dt = T/M
t = Constant(0)
a = Constant(1/(2*pi**2))
b = Constant([0, 0])
f = Constant(0)
mesh = UnitSquareMesh(N, N)
x, y = SpatialCoordinate(mesh)
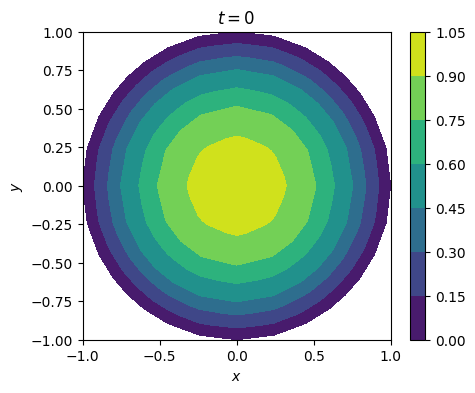
u_0 = sin(pi*x)*sin(pi*y)
V = FunctionSpace(mesh, 'CG', 1)
u_trial, u_test = TrialFunction(V), TestFunction(V)
u_n = Function(V, name='u_n')
u_h = Function(V, name='u_h')
bc = DirichletBC(V, 0, 'on_boundary')
A = (
1/dt*(u_trial - u_n)*u_test*dx
+ inner(grad(u_trial), b*u_test)*dx
+ inner(a*grad(u_trial), grad(u_test))*dx
- f*u_test*dx
)
problem = LinearVariationalProblem(lhs(A), rhs(A), u_h, bcs=bc)
solver = LinearVariationalSolver(problem)
u_h.project(u_0)
# u_h.interpolate(u_0)
u_n.assign(u_h)
plot_solution(u_h, time=0)
# output = VTKFile('result.pvd', adaptive=True)
# output.write(u_h, time=0)
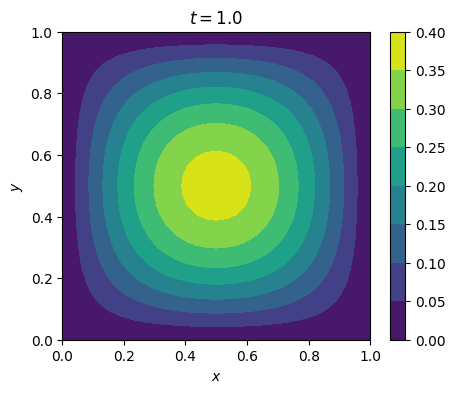
for i in range(M):
t.assign((i+1)*dt)
solver.solve()
u_n.assign(u_h)
# output.write(u_h, time=float(t))
plot_solution(u_h, time=float(t))

3.1.2. Run the code#
Save the code to file heat.py, and run it as follows.
python heat.py
mpiexec -n 4 python heat.py
Add command line options
petsc options
custom options
3.1.3. View results in paraview#
Download paraview from https://www.paraview.org/download/.
3.2. 移动边界问题#
from firedrake import *
from firedrake.pyplot import tricontourf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_solution(u_h, time=None, vmin=None, vmax=None):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=[5, 4])
if vmin is None or vmax is None:
levels = None
else:
levels = np.linspace(vmin, vmax, 11)
cs = tricontourf(u_h, axes=ax, levels=levels)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlabel('$x$')
ax.set_ylabel('$y$')
if time is not None:
ax.set_title(f'$t={time}$')
cbar = fig.colorbar(cs)
T = 1
M = 32
dt = 1/M
a = Constant(1)
b = as_vector([0, 0]) # vector([0, 0, 0])
t = Constant(0)
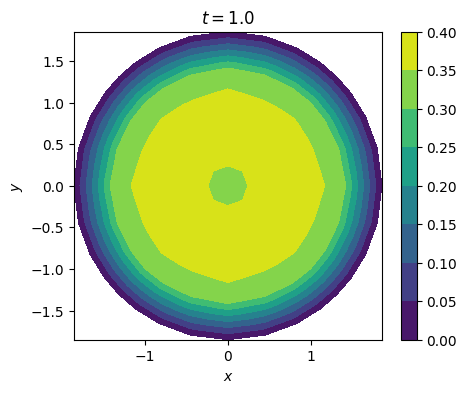
mesh = UnitDiskMesh(2)
# mesh = Mesh(gmshfile)
x, y = SpatialCoordinate(mesh)
f = x**2 + y**2
u_0 = 1 - x**2 - y**2
v = as_vector([x, y])*exp(-t)
V_coords = VectorFunctionSpace(mesh, 'CG', 1)
w_vel = Function(V_coords)
V = FunctionSpace(mesh, 'CG', 1)
u_trial, u_test = TrialFunction(V), TestFunction(V)
u_n = Function(V, name='u_n')
u_h = Function(V, name='u_h')
bc = DirichletBC(V, 0, 'on_boundary')
A = (
1/dt*(u_trial - u_n)*u_test*dx
+ inner(grad(u_trial), u_test*(b - w_vel))*dx
+ inner(a*grad(u_trial), grad(u_test))*dx
- f*u_test*dx
)
problem = LinearVariationalProblem(lhs(A), rhs(A), u_h, bcs=bc)
solver = LinearVariationalSolver(problem)
w_trial, w_test = TrialFunction(V_coords), TestFunction(V_coords)
bc_move_mesh = DirichletBC(V_coords, v, 'on_boundary')
B = inner(grad(w_trial), grad(w_test))*dx - Constant(0)*w_test[0]*dx
mm_problem = LinearVariationalProblem(lhs(B), rhs(B), w_vel, bcs=bc_move_mesh)
mm_solver = LinearVariationalSolver(mm_problem)
u_h.project(u_0)
# u_h.interpolate(u_0)
u_n.assign(u_h)
# output = VTKFile('result.pvd', adaptive=True)
# output.write(u_h, time=0)
plot_solution(u_h, time=0)
for i in range(M):
t.assign((i+1)*dt)
mm_solver.solve()
mesh.coordinates.assign(mesh.coordinates + dt*w_vel)
solver.solve()
u_n.assign(u_h)
# output.write(u_h, time=(i+1)*dt)
plot_solution(u_h, time=M*dt)